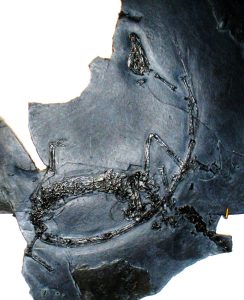
Scientists have been studying how a prehistoric creature named Tanystropheus supported its insanely long neck.
Fossils of this remarkable reptile, which roamed the planet’s coastal regions some 242 million years ago, were first discovered in the mid 19th-Century.
Since then, palaeontologists have speculated over whether the animal – which had a ridiculously long neck three times the length of its own body – lived predominantly on land or in water.
Now though, a new study by Dr Nick Fraser of National Museums Scotland, and colleagues, has finally shed some light on the mystery.

By using modern high-resolution micro-CT scans of the fossils to construct a detailed computer model of the creature’s skull, the researchers were able to determine that Tanystropheus had nostrils on the top of its snout and teeth designed primarily for trapping fish, indicating that it most likely spent the majority of its life in the water.
This also helps to explain how it was able to support the weight of its huge neck.
That said, it is also likely that the species did spend some time out of the water as well.
“Our group feels that this animal was an aquatic animal most of the time,” said Fraser.
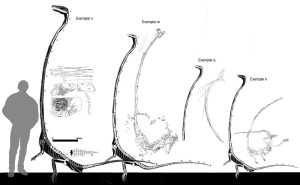
With its incredibly long but relatively stiff neck,Tanystropheus has been often proposed and reconstructed as an aquatic or semi-aquatic reptile, a theory supported by the fact that the creature is most commonly found in semiaquatic fossil sites wherein known terrestrial reptile remains are scarce. Tanystropheus is most often considered to have been piscivorous (or ‘fish-eating’), due to the presence of a long, narrow snout sporting sharp interlocking teeth. In several young specimens, three-cusped cheek teeth are present in the jaw, which might indicate an insectivorous diet; however, similar teeth patterns have been found in Eudimorphodon and Langobardisaurus, both of whom are considered piscivores. Additionally, hooklets from cephalopod tentacles and what may be fish scales have been found near the belly regions of some specimens.